| [1] Pawelec KM, Best SM, Cameron RE. Collagen: a network for regenerative medicine. J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med. 2016; 4(40):6484-6496. [2] Sellem PH, Caranzan FR, Bene MC, et al. Immunogenicity of Injectable Collagen Implants. Dermatol Surg. 2013;13(11): 1199-1203. [3] Delgado L, Bayon Y, Pandit A, et al. To cross-link or not to cross-link? Cross-linking associated foreign body response of collagen-based devices. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21(3):298. [4] Avila RM, Rodriguez BL, Sanchez ML. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018;17(1):20-26. [5] 温慧芳,陈丽丽,白春清,等.基于不同提取方法的鮰鱼皮胶原蛋白理化性质的比较研究[J].食品科学,2016,37(1):74-81.[6] 刘迪,王利强,任莹.猪跟腱胶原蛋白酶法提取工艺的研究[J].食品工业,2017,39(10):72-77.[7] 冯文婕,赵粼,阙斐.酸酶复合法优化鱼鳞胶原蛋白的提取工艺[J].湖北农业科学,2016,55(5):1242-1246.[8] 黄雯.鮰鱼鱼皮和鲅鱼鱼皮胶原蛋白的提取与性质研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学,2015.[9] He J, Ma X, Zhang F, et al. New strategy for expression of recombinant hydroxylated human collagen α1(III) chains in Pichia pastoris GS115. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2015;62(3):293-299. [10] 李伟娜,尚子方,段志广,等.毕赤酵母高密度发酵产Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白及其胃粘膜修复功能[J].生物工程学报, 2017,33(4):672-682.[11] Kumar VA, Taylor NL, Jalan AA, et al. A nanostructured synthetic collagen mimic for hemostasis. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(4): 1484-1490. [12] 雷静,李奕恒,刘旭昭,等.动物源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白可引起BALB/c小鼠细胞免疫反应和组织免疫毒性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(34): 5506-5512.[13] 王建华,贺超龙,程娘梅,等.无花果蛋白酶去除牛腱Ⅰ型胶原蛋白末端肽的工艺研究[C].第六届全国组织工程与再生医学大会, 2013.[14] Peng YY, Glattauer V, Ramshaw JA, et al. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and cell compatibility of avian collagen for biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2010; 93(4):1235. [15] 李晓辉,倪赛巧,王翀,等.超高压及酶解对虹鳟鱼Ⅰ型胶原蛋白抗原性的影响[EB/OL]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20180323.1016.088.html.2018-03-23.[16] 宫妍婕,王龙,董来东,等.不同冻存液及降温方式对心脏瓣膜组织学及免疫原性的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2016,54(8):44-49.[17] 李毅,王洪瑾.牛跟腱胶原蛋白提取工艺的生物安全性研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2017,28(10):623-626.[18] 盛嘉隽.重组人胶原纳米纤维支架的制备及其生物相容性检测[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017.[19] Jab?ońskatrypu? A, Matejczyk M, Rosochacki S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016;23(sup1):177-183. [20] 符锋,秦喆,李晓红,等.胶原/壳聚糖复合支架植入大鼠不同部位降解速率的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):864-870.[21] Rahmanian-Schwarz A, Held M, Knoeller T, et al. In vivo biocompatibility and biodegradation of a novel thin and mechanically stable collagen scaffoldJ Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(4):1173-1179. [22] Davidenko N, Bax DV, Schuster CF, et al. Optimisation of UV irradiation as a binding site conserving method for crosslinking collagen-based scaffolds. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(1):14. [23] Bellincampi LD, Dunn MG. Effect of crosslinking method on collagen fiber‐fibroblast interactions. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015; 63(11):1493-1498. [24] 张义.不同交联剂对胶原蛋白可食膜性能的影响[D]. 天津:天津科技大学,2016.[25] Perez-Puyana V, Romero A, Guerrero A. Influence of collagen concentration and glutaraldehyde on collagen-based scaffold properties. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6):1462-1468. [26] Zhou X, Tao Y, Chen E, et al. Genipin-cross-linked type II collagen scaffold promotes the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into nucleus pulposus-like cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106(5):1258-1268. [27] Gao S, Yuan Z, Guo W, et al. Comparison of glutaraldehyde and carbodiimides to crosslink tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by decellularized porcine menisci. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;71: 891-900. [28] Cholas R, Kunjalukkal P S, Gervaso F, et al. Scaffolds for bone regeneration made of hydroxyapatite microspheres in a collagen matrix Mater Sci Eng C. 2016, 63:499-505. [29] Baheiraei N, Nourani MR, Mortazavi S, et al. Development of a bioactive porous collagen/beta-tricalcium phosphate bone graft assisting rapid vascularization for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(1):73-85. [30] Long T, Yang J, Shi SS, et al. Fabrication of three-dimensional porous scaffold based on collagen fiber and bioglass for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(7):1455-1464. [31] Raftery RM, Woods B, Marques ALP, et al. Multifunctional Biomaterials from the Sea: Assessing the effects of Chitosan incorporation into Collagen Scaffolds on Mechanical and Biological Functionality. Acta Biomaterialia. 2016;43:160-169. [32] 鲁瑶.可吸收胶原蛋白止血海绵在腔镜甲状腺手术中的止血疗效[J].中国医药科学,2014,4(17):196-197.[33] Ramanathan G, Singaravelu S, Muthukumar T, et al. Design and characterization of 3D hybrid collagen matrixes as a dermal substitute in skin tissue engineering Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;72:359-370. [34] 雷静,刘旭昭,陈淡嫦,等.凝胶型胶原敷料修复糖尿病皮肤缺损及促进血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(52):8456-8462.[35] 罗心凯,陈治标,陈谦学.免缝胶原海绵人工硬脑膜在颅脑损伤大骨瓣减压术中的应用[J].中国临床神经外科杂志, 2016,21(6):357-358.[36] Du T, Niu X, Li Z, et al. Crosslinking induces high mineralization of apatite minerals on collagen fibers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113: 450-457. [37] Shi XD, Chen LW, Li SW, et al. The observed difference of RAW264. 7 macrophage phenotype on mineralized collagen and hydroxyapatite. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):041001. [38] 芶印尧,祝少博.可注射性生物复合材料修复老年膝关节软骨损伤的应用分析[J].实用药物与临床,2017,20(3):280-283.[39] Wang Y, Hua Y, Zhang Q, et al. Using biomimetically mineralized collagen membranes with different surface stiffness to guide regeneration of bone defects. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(7):1545-1555. [40] Hall BI, Paladino E, Szabo P, et al. Electrospun collagen-based nanofibres: A sustainable material for improved antibiotic utilisation in tissue engineering applicationsInt J Pharm. 2017; 531(1):67-79. [41] Chen Y, Kawazoe N, Chen G. Preparation of dexamethasone- loaded biphasic calcium phosphate nanoparticles/collagen porous composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;67:341-353. [42] Sun X, Wang J, Wang Y, et al. Collagen-based porous scaffolds containing PLGA microspheres for controlled kartogenin release in cartilage tissue engineering. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017:1-10. [43] Chan EC, Kuo SM, Kong AM, et al. Three Dimensional Collagen Scaffold Promotes Intrinsic Vascularisation for Tissue Engineering Applications. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149799. [44] Hoogenkamp HR, Pot MW, Hafmans TG, et al. Scaffolds for whole organ tissue engineering: Construction and in vitro evaluation of a seamless, spherical and hollow collagen bladder construct with appendices. Acta Biomater. 2016;43:112-121. [45] Nguyen BB, Moriarty RA, Kamalitdinov T, et al. Collagen hydrogel scaffold promotes mesenchymal stem cell and endothelial cell coculture for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(4):1123-1131. [46] Lee H, Yang GH, Kim M, et al. Fabrication of micro/nanoporous collagen/dECM/silk-fibroin biocomposite scaffolds using a low temperature 3D printing process for bone tissue regeneration Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;84:140-147. [47] Yang X, Lu Z, Wu H, et al. Collagen-alginate as bioink for three-dimensional (3D) cell printing based cartilage tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;83:195-201. [48] 唐洪,刘俊利,朱长宝,等.碳化二亚胺作为胶原蛋白交联剂的生物安全性评价[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(10):2510-2513.[49] 谢玥,王晨,邱东.戊二醛对成骨细胞毒性的研究[J].明胶科学与技术, 2014,34(3):130-135.[50] Casali DM, Yost MJ, Matthews MA. Eliminating Glutaraldehyde from Crosslinked Collagen Films using Supercritical CO2. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2017;106(1):86-94. [51] 夏磊磊,毅陈,门福民,等.不同组织来源的胶原蛋白生物材料物理性能对比研究[J].材料科学,2017,7(4):431-439.[52] 阮功成,曹慧,徐斐,等.不同来源胶原蛋白抗冻活性的研究[J].食品科学,2014,35(17):22-26.[53] Drzewiecki KE, Malavade JN, Ahmed I, et al. A thermoreversible, photocrosslinkable collagen bio-ink for free-form fabrication of scaffolds for regenerative medicine Technology (Singap World Sci). 2017;5(4):185-195. |
.jpg)

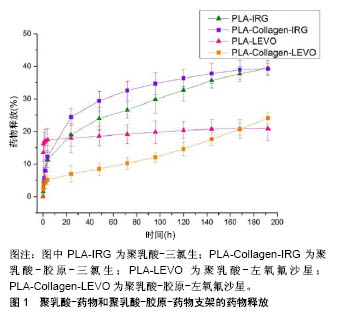
.jpg)